Achieving Organizational Compliance with AWS Config Conformance Packs: Methodology, Implementation, and Lifecycle Management
Introduction
Organizations seeking robust governance and compliance in AWS environments increasingly rely on AWS Config Conformance Packs. These packs are a part of AWS Config, a service that allows users to assess, audit, and evaluate the configurations of AWS resources. Conformance Packs extend this functionality by enabling organizations to create a set of AWS Config rules and remediation actions as a single pack, simplifying the management and deployment of compliance standards across multiple accounts and regions.
AWS Config Conformance Packs provide a scalable way to enforce compliance standards and automate remediation across AWS accounts. This approach ensures that organizations can meet regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOC 2, while maintaining operational efficiency and audit readiness. By grouping AWS Config Rules (managed or custom) and remediation actions (manual or automated, primarily configured as AWS Systems Manager Documents), Conformance Packs streamline compliance monitoring and remediation.
How AWS Conformance Packs Work
The process operates as follows:
- Continuous Monitoring: AWS Config continuously monitors AWS resources. The Conformance Pack uses its Config Rules to evaluate resources and marks them as non-compliant if they do not meet the evaluation criteria.
- Automated Remediation: If a resource is marked as non-compliant and the rule has an automated remediation action, AWS Systems Manager executes the corresponding action using the configured Systems Manager Document.
- Re-evaluation: The remediation status is reported back to AWS Config, which then reevaluates the rule and updates the resource’s compliance status.
Prerequisites and Foundational References
Before implementing Conformance Packs, several prerequisites must be met:
- AWS Config Recording: Ensure AWS Config recording is enabled across all accounts and regions.
- Service Roles: A service role for AWS Config Conformance Packs (
AWSServiceRoleForConfigConforms) must exist. If remediation actions are used, a service role for AWS Config remediation is also required. - S3 Bucket: An Amazon S3 bucket must be available for storing and delivering pack compliance results, with access granted to the service role.
- AWS Organizations Setup: Establish a management account and member accounts (e.g., production, development, security) to centralize governance and enable cross-account monitoring.
Methodology for Conformance Pack Implementation
Discovery and Requirements Analysis
The process begins with stakeholder workshops to capture compliance requirements, such as encryption mandates or access controls. A current state assessment is performed using AWS Config Aggregator to identify configuration gaps and non-compliant resources. Findings are documented for traceability and audit purposes.
Control Derivation and Policy Mapping
Compliance requirements are mapped to AWS managed rules and Control Tower guardrails. Where managed rules are insufficient, custom Lambda-backed Config Rules are developed. Rules are grouped into logical Conformance Packs (e.g., Security Compliance Pack, Operational Compliance Pack) for reusability and auditability.
Tooling and Governance Workflow
Conformance Packs are authored in YAML templates, stored in version-controlled repositories (e.g., AWS CodeCommit, GitHub), and deployed via CI/CD pipelines (AWS CodePipeline, GitHub Actions). Automated testing, peer reviews, and audit logs ensure governance and traceability.
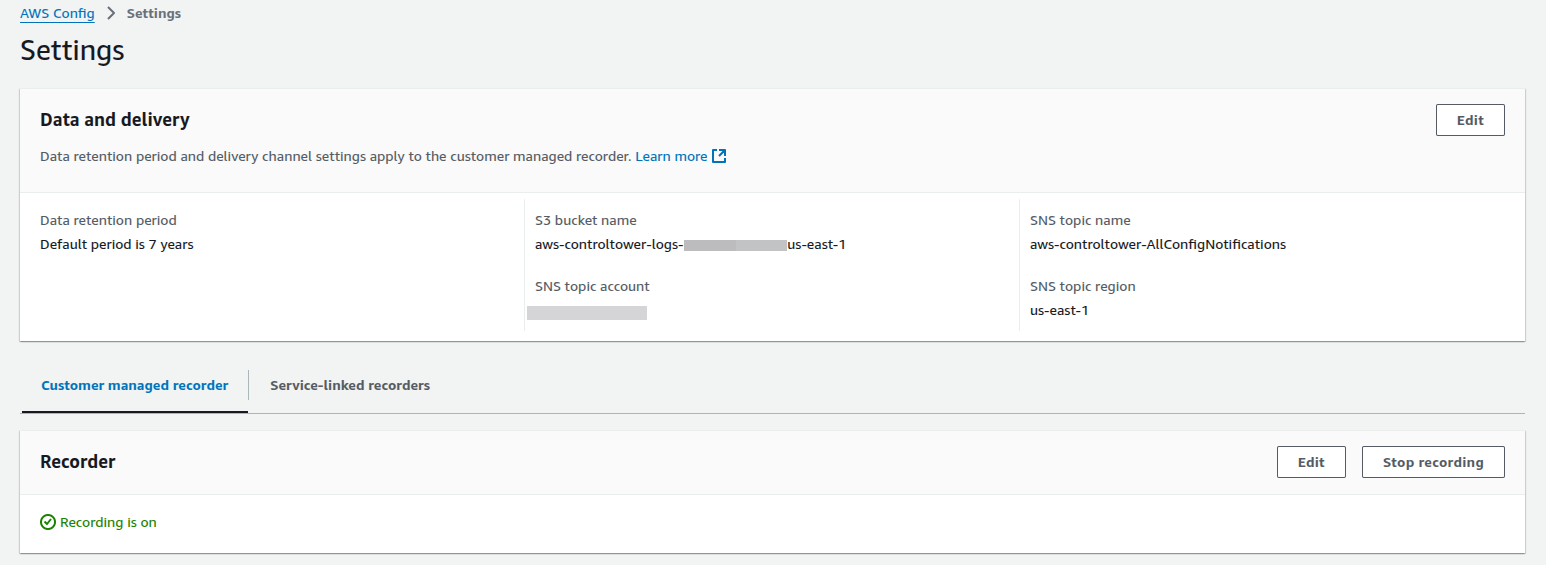
Fig: Config Recorder is On
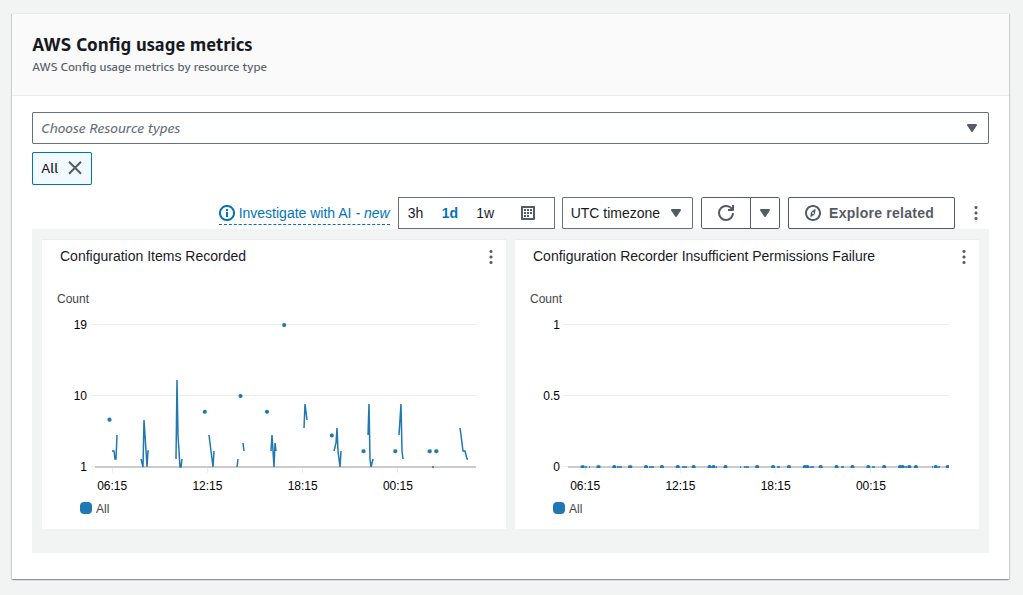
fig: AWS Config Usage Metrics
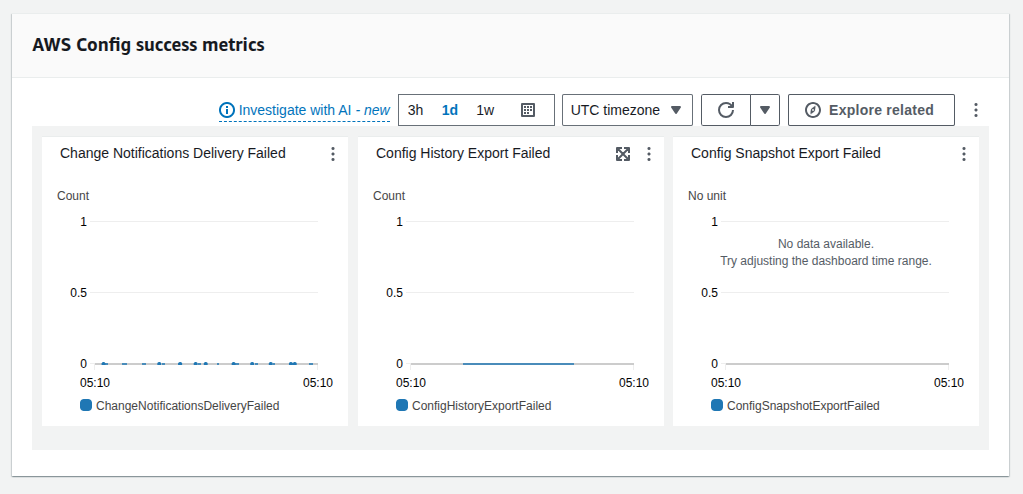
fig: Config Success Metrics
fig: AWS Config Aggregator
Key Components
AWS Config Rules
- Managed Rules: Address common compliance scenarios (e.g., EBS encryption, S3 public access).
- Custom Rules: Implemented with Lambda functions for organization-specific requirements.
Remediation Actions
- AWS Systems Manager Documents: Automate remediation (e.g., encrypting EBS volumes).
- Lambda Functions: Handle complex remediations (e.g., updating S3 bucket policies).
YAML Templates
Templates define rule parameters, remediation actions, and deployment configurations, enabling repeatable and consistent deployments.
Implementation Steps
Step 1: Configure Multi-Account Environment
- Enable AWS Config Across Accounts: Deploy AWS Config in each member account and region using AWS Organizations. Configure an S3 bucket per account (
s3://config-bucket-123456789012-us-east-1) with versioning enabled to store configuration snapshots. Assign an IAM role (e.g.,AWSConfigRole) with policies allowingconfig:Put*ands3:PutObjectactions. - Set Up Aggregator: In the management account, create an AWS Config Aggregator to consolidate data. Define an aggregator named
OrgWideComplianceAggregatorwith a scope covering all accounts and regions. Use an IAM role (e.g.,AWSConfigAggregatorRole) withconfig:Describe*permissions across accounts - IAM Permissions: Ensure cross-account access by attaching the
AWSConfigRoleForOrganizationspolicy to the aggregator role, allowing it to read Config data from member accounts.
Step 2: Author and Validate Conformance Pack
- YAML Template Development: Create a YAML file (e.g.,
security-compliance-pack.yaml) defining the Conformance Pack. Include rules likeencrypted-volumes,s3-bucket-public-read-prohibited,root-account-mfa-enabled, andacm-certificate-expiration-checkwith adaysToExpirationparameter of 14. Add remediation actions, such as an SSM document for S3 public access correction. - Validation: Use the AWS CLI to validate the template syntax:
aws configservice validate-conformance-pack --conformance-pack-template-s3-uri s3://my-template-bucket/security-compliance-pack.yaml
Review the output for errors and adjust accordingly
Step 3: Deploy Conformance Pack
-
Git Repository: Commit the validated YAML to a Git repository ( https://github.com/my-org/conformance-packsConnect your Github account ).
-
CI/CD Pipeline: Configure AWS CodePipeline with stages for source (GitHub), build (validation), and deploy (StackSet). Use a buildspec file to execute:
phases: build: commands: - aws configservice put-conformance-pack --conformance-pack-name SecurityCompliancePack --template-s3-uri s3://my-template-bucket/security-compliance-pack.yamlDeploy the StackSet to all member accounts and regions via AWS Organizations
-
Manual Deployment (Alternative): For testing, deploy manually using:
aws configservice put-conformance-pack --conformance-pack-name SecurityCompliancePack --template-s3-uri s3://my-template-bucket/security-compliance-pack.yaml --delivery-s3-bucket my-config-delivery-bucket
Step 4: Monitor and Validate Compliance
- Aggregator Dashboard: Access the AWS Config Aggregator in the management account to view compliance status across all accounts. Filter by rule name or account ID to identify non-compliant resources
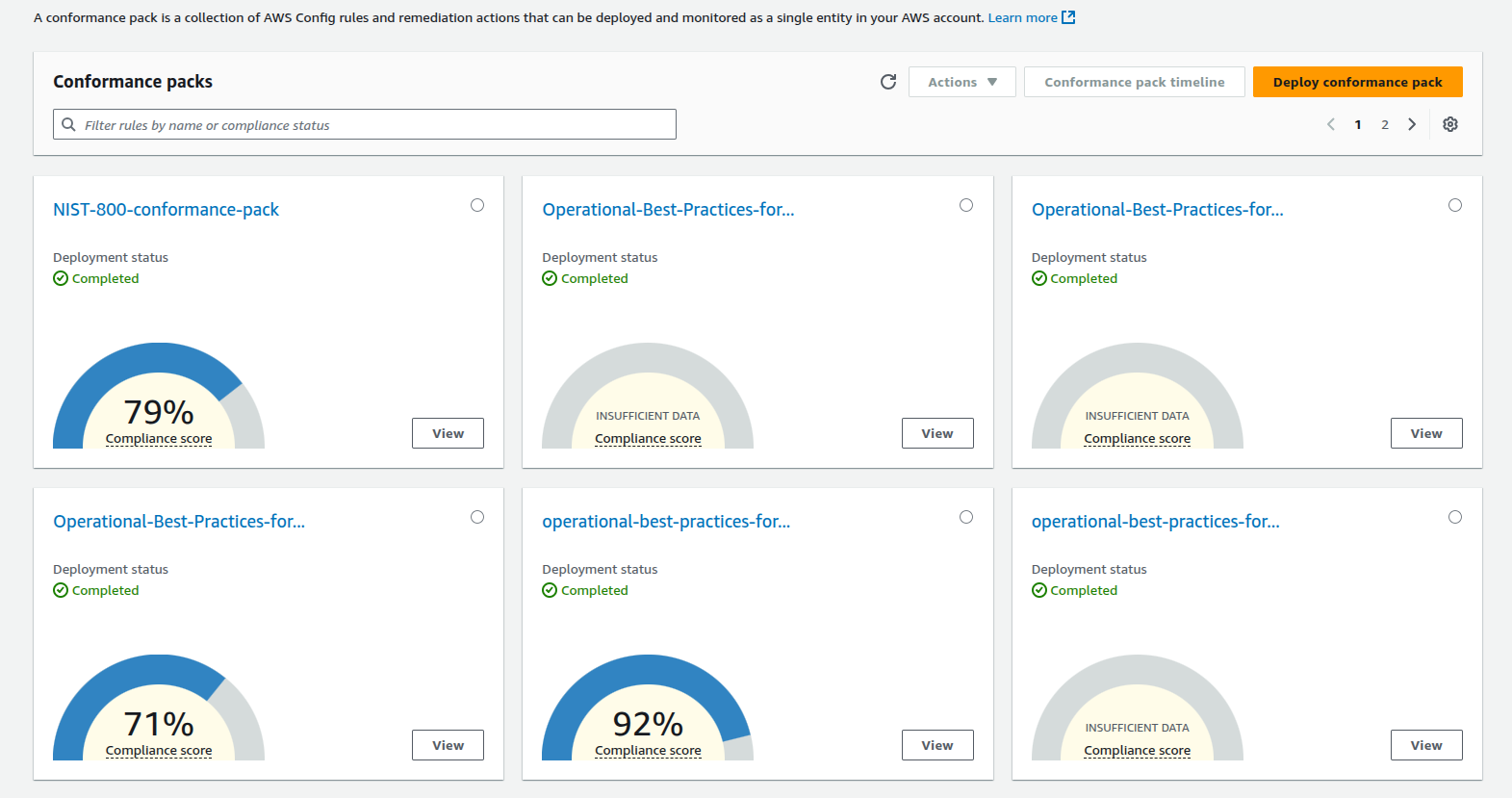
fig: Conformance Pack
- SNS Notifications: Configure an Amazon SNS topic in the management account to receive notifications for non-compliant resources. Subscribe email or Lambda endpoints to the topic, ensuring real-time alerts
- Testing: Simulate non-compliance (e.g., create an
unencrypted EBS volumein a member account) and verify that the rule flags it asNON_COMPLIANTwith an annotation like “EBS volume is not encrypted.” Test remediation by triggering the associated SSM document and confirming the volume is encrypted
Lifecycle Management
Updates and Versioning
Changes to Conformance Packs are managed through version-controlled repositories and redeployed via CI/CD pipelines. Rollbacks are supported by reverting to previous commits.
Monitoring and Reporting
Compliance data is regularly reviewed in the AWS Config Console or exported via CLI for audit reporting. S3 lifecycle policies ensure evidence retention for regulatory requirements.
Decommissioning
Obsolete Conformance Packs are deleted using AWS CLI, and YAML templates are archived with decommissioning notes.
Audit Trail
Centralized S3 buckets store configuration history and compliance statuses, providing a robust audit trail for regulatory reviews.
Alignment with Compliance Objectives
The Conformance Pack implementation enables:
- Detection of Non-Compliance: Proactive identification of issues across accounts.
- Automated Remediation: Reduced manual effort through automation.
- Audit-Ready Evidence: Centralized data for regulatory verification.
Conclusion
Implementing AWS Config Conformance Packs delivers a technically robust and scalable framework for compliance in multi-account AWS environments. Through structured discovery, control derivation, automated deployment, and comprehensive lifecycle management, organizations achieve consistent governance, scalability, and auditability, making Conformance Packs indispensable for managing distributed AWS infrastructures.
Stay tuned for more. Let’s connect on Linkedin and explore my GitHub for future insights.